Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Other Known Aliases – tibial tubercle apophysitis
Definition – traction apophysitis of the proximal tibial tubercle at the insertion of the patellar tendon.
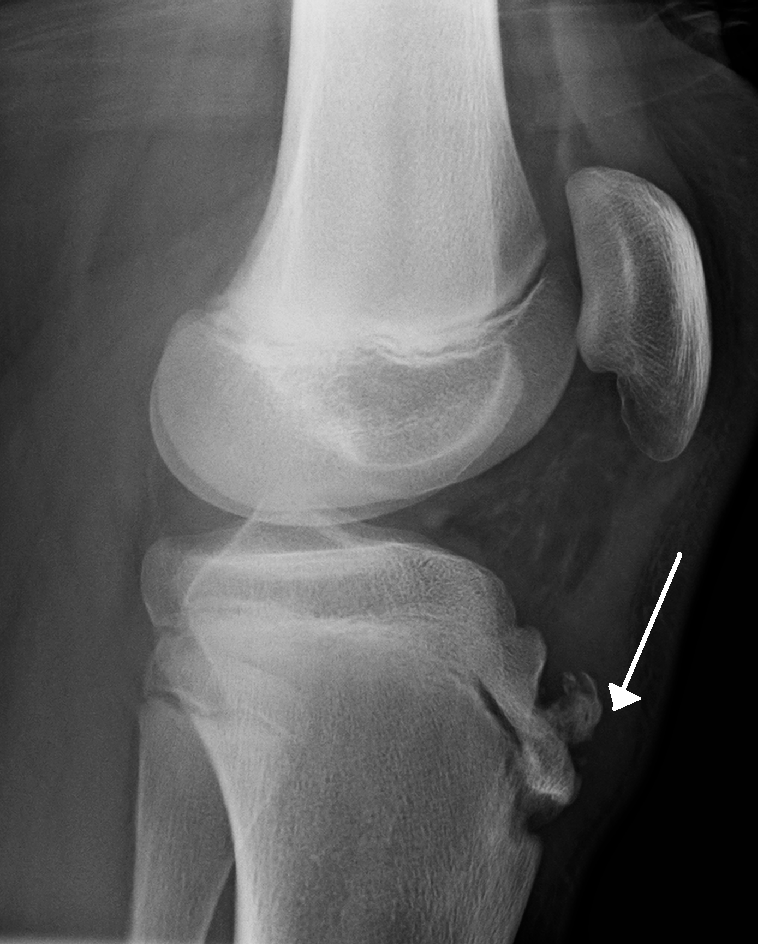
Clinical Significance – Most commonly occurs in adolescents as a result of overuse stress in athletics requiring explosive running, jumping, or cutting. This places an extreme amount of stress on the tibial tubercle and may lead to a chronic avulsion. As the new healing callous is laid down, a pronounced deformity may develop.

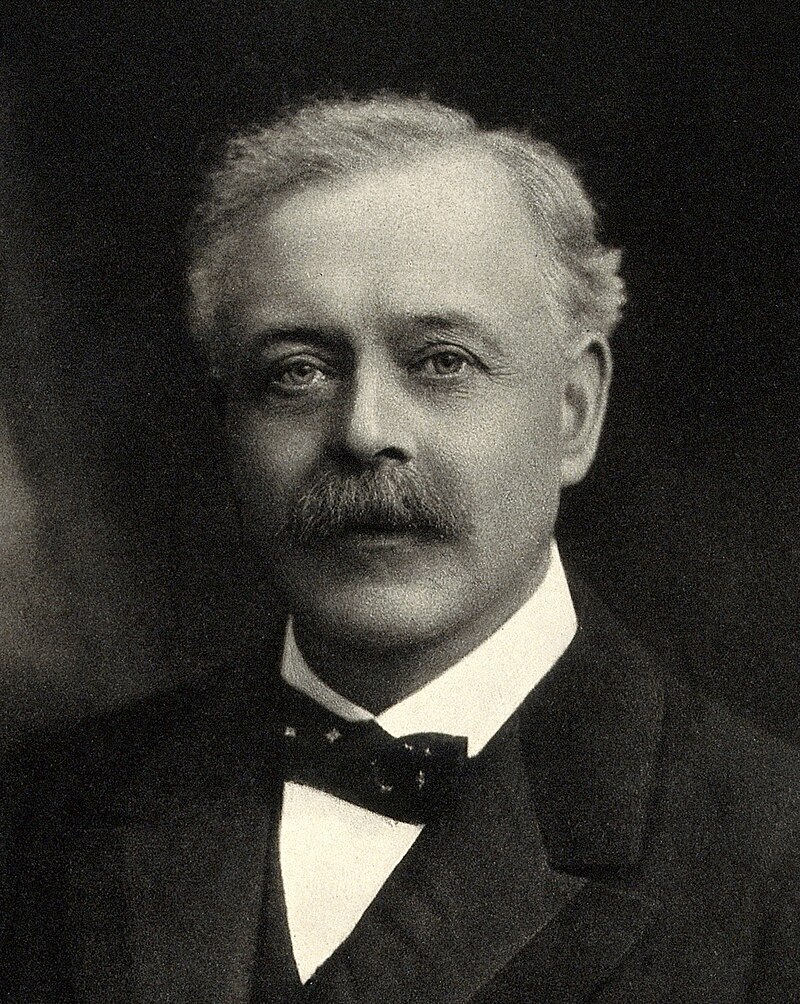
History – Named after two physician who contemporaneously published on this condition in the same year. Robert Bayley Osgood (1873-1956), was an American orthopaedic surgeon, and received his medical doctorate from Harvard University in 1899. Dr. Osgood spent his entire career practicing in Boston at Massachusetts General Hospital and teaching at the Harvard Medical School. Carl Schlatter (1863-1934), was a Swiss physician and surgeon, and received his medical doctorate from the University of Zurich in 1889. Dr. Schlatter was a skilled surgeon and had a primary interest in trauma and causality medicine during World War I. Both physicians were well respected educators and professors of their time and both published their findings of this condition in 1903.

Osgood 

Schlatter 
References
- Firkin BG and Whitwirth JA. Dictionary of Medical Eponyms. 2nd ed. New York, NY; Parthenon Publishing Group. 1996.
- Bartolucci S, Forbis P. Stedman’s Medical Eponyms. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD; LWW. 2005.
- Yee AJ, Pfiffner P. (2012). Medical Eponyms (Version 1.4.2) [Mobile Application Software]. Retrieved http://itunes.apple.com.
- Whonamedit – dictionary of medical eponyms. http://www.whonamedit.com
- Up To Date. www.uptodate.com
- Osgood RB. Lesions of the tibia tubercle occurring during adolescence.
Boston Medical and Surgical Journal. 1903;148: 114-117. [article] - Schlatter CB. Verletzungen des schnabelförmigen Forsatzes der oberen Tibiaepiphyse. Beiträge zur klinischen Chirurgie, 1903;38: 874-887. [article]